Technical SEO focuses on optimizing the technical elements of your website to improve its search engine visibility and performance. While on-page SEO and content strategies are crucial for ranking, technical SEO forms the foundation that allows search engines to crawl, index, and rank your site efficiently. Without a solid technical SEO strategy, even the best content can struggle to rank.
In this guide, we’ll explore essential technical SEO strategies that can boost your website performance and help you achieve better search engine rankings.
1. Optimize Website Crawling and Indexing
Crawling and indexing are the processes search engines use to discover and categorize the pages on your website. Ensuring that search engines can efficiently crawl and index your site is the foundation of technical SEO.
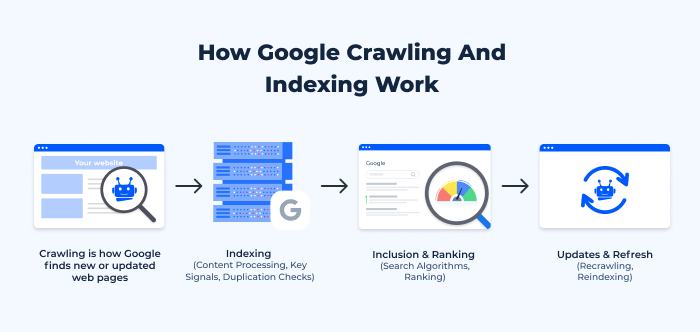
Actionable Steps:
- Submit an XML Sitemap: An XML sitemap provides search engines with a roadmap of your website’s structure. Submit your sitemap to Google Search Console and Bing Webmaster Tools to help search engines identify your most important pages.
- Ensure Proper Robots.txt Configuration: The robots.txt file controls which pages search engines can crawl. Ensure you’re not accidentally blocking important pages from being crawled.
- Use Canonical Tags: If you have duplicate or similar content, use canonical tags to tell search engines which version of a page is the authoritative one. This helps prevent duplicate content issues and consolidates ranking signals.
2. Improve Website Speed and Performance
Page speed is a critical ranking factor, especially after the rollout of Google’s Core Web Vitals. Slow-loading websites not only frustrate users but also rank lower in search results.

Actionable Steps:
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN): A CDN helps reduce latency by serving your website’s content from servers located closer to your users. This improves load times, especially for users far from your server’s location.
- Optimize Images: Compress and resize images without compromising quality using tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim. Use modern formats like WebP for further performance gains.
- Leverage Browser Caching: Set your server to cache static resources, such as images and CSS files, so they load faster for returning visitors.
- Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML: Minification removes unnecessary characters and spaces from your code, making it smaller and faster to load.
- Measure with Core Web Vitals: Regularly test your site using tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights or Lighthouse to monitor your Core Web Vitals: Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Aim for an LCP under 2.5 seconds, an FID of less than 100 milliseconds, and minimal CLS.
3. Implement Mobile-First Optimization
Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it predominantly uses the mobile version of your website for ranking and indexing. If your website isn’t mobile-friendly, it will negatively affect your rankings, especially in mobile search results.
Actionable Steps:
- Use Responsive Design: Ensure your site is fully responsive, meaning it adjusts to fit different screen sizes. This improves user experience across all devices and helps with mobile rankings.
- Test Your Site’s Mobile Usability: Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test to check if your site is optimized for mobile. Ensure that text is legible without zooming, buttons are easily clickable, and the layout adapts smoothly.
- Prioritize Mobile Page Speed: Since mobile users are often on slower connections, optimizing for mobile speed is crucial. Remove unnecessary scripts, enable lazy loading, and keep the mobile site lightweight.
4. Ensure HTTPS for Secure Browsing
Security is a ranking factor in Google’s algorithm, and having an HTTPS website is essential for both user trust and SEO performance. HTTPS encrypts data exchanged between your website and visitors, ensuring secure browsing.
Actionable Steps:
- Install an SSL Certificate: If you haven’t already, install an SSL certificate on your website. This ensures that your site uses HTTPS instead of HTTP.
- Redirect HTTP to HTTPS: After installing SSL, set up a 301 redirect from HTTP to HTTPS to avoid duplicate content issues and ensure that users land on the secure version of your site.
- Monitor Mixed Content Issues: Ensure that all your page elements (e.g., images, scripts, CSS) load via HTTPS. Mixed content (HTTP and HTTPS elements on the same page) can lead to security warnings and affect user experience.
5. Optimize for Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals are a set of performance metrics introduced by Google to measure the quality of user experience on your website. These metrics focus on three key areas: page loading, interactivity, and visual stability.
Actionable Steps:
- Improve Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Optimize your site to ensure the largest visible element on a page (e.g., an image, video, or large block of text) loads within 2.5 seconds.
- Enhance First Input Delay (FID): Reduce the time it takes for your site to respond to user interactions. Optimize JavaScript execution, use lazy loading, and minimize third-party scripts to improve FID.
- Fix Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Avoid unexpected layout shifts during page load by specifying image dimensions and avoiding dynamic content that loads late. Aim for a CLS score of less than 0.1 to minimize layout instability.
6. Structured Data and Schema Markup
Structured data and schema markup help search engines understand the content on your website more effectively. Using structured data can also enhance your search listings with rich snippets, which improve click-through rates (CTR).
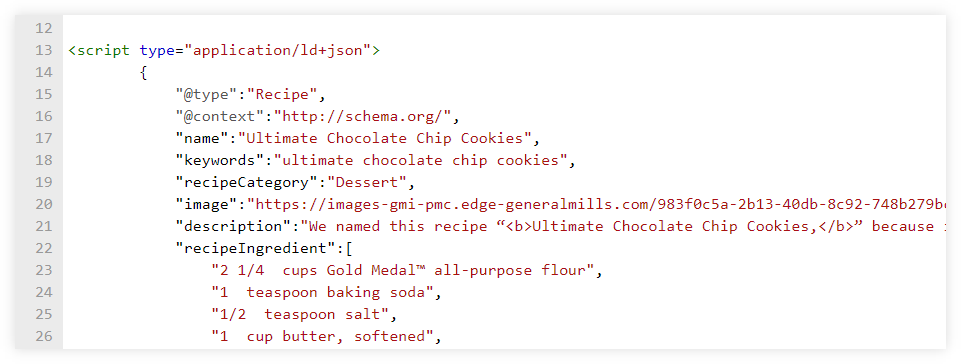
Actionable Steps:
- Add Schema Markup to Key Pages: Use schema.org vocabulary to mark up important data like reviews, product information, events, and business details. This can help search engines display rich results in SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages).
- Test Structured Data with Google’s Rich Results Tool: After implementing structured data, test it with Google’s Rich Results Testing Tool to ensure it’s error-free and correctly implemented.
- Use JSON-LD Format: Google recommends using JSON-LD for structured data implementation, as it is the easiest to add and update without affecting your HTML structure.
7. Fix Crawl Errors and Broken Links
Crawl errors can prevent search engines from accessing important pages on your site, while broken links lead to poor user experience and can hurt your SEO performance.
Actionable Steps:
- Monitor Crawl Errors in Google Search Console: Regularly check Google Search Console for crawl errors. Fix any 404 errors (not found) or 500 errors (server issues) that prevent search engines from accessing your pages.
- Fix Broken Internal Links: Use tools like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs to identify broken internal links. Replace or remove these links to ensure users and search engines can navigate your site without hitting dead ends.
- Implement 301 Redirects for Moved Pages: If you’ve removed or moved a page, always implement a 301 redirect to direct users and search engines to the new URL. This helps preserve your SEO equity.
8. Optimize URL Structure
A clean and descriptive URL structure is not only more user-friendly but also helps search engines understand the context of your pages.
Actionable Steps:
- Use Short, Descriptive URLs: Ensure your URLs are concise, descriptive, and include relevant keywords. Avoid long strings of numbers, symbols, or irrelevant characters.
- Maintain a Consistent URL Structure: Follow a logical structure for your URLs. For example, use /category/subcategory/product for eCommerce sites.
- Avoid Dynamic URLs When Possible: Static URLs with keywords (e.g., /best-laptops) are more SEO-friendly than dynamic URLs with query strings (e.g., /?p=1234).
9. Implement Pagination and Hreflang Tags for International SEO
For websites targeting multiple regions or languages, proper implementation of hreflang and pagination tags is essential to avoid duplicate content issues and ensure the correct version of your site is shown to the right users.
Actionable Steps:
- Use Hreflang Tags for Multilingual Sites: Hreflang tags tell search engines which language or region a specific page targets. For example, hreflang=”en-us“ indicates English content for users in the U.S., while hreflang=”fr-ca” targets French speakers in Canada.
- Implement Pagination Correctly: For paginated content (e.g., multi-page blog posts or product category pages), use rel=”next” and rel=”prev” to help search engines understand the relationship between pages.
Conclusion
Implementing these technical SEO strategies is crucial to improving your website’s overall performance, user experience, and search engine visibility. By optimizing website crawling and indexing, improving page speed, ensuring mobile-first design, and fixing crawl errors, you create a solid foundation for long-term SEO success.
These technical improvements may not always be visible to the end user, but they play a key role in ensuring search engines can efficiently crawl, index, and rank your site, giving you a competitive edge in search rankings.


